Alpine ecosystems, found in high mountain regions, are sensitive to climate change. Warming temperatures lead to reduced snow cover and shifting vegetation zones, threatening species adapted to cold environments.
Blue carbon refers to carbon captured by the world’s ocean and coastal ecosystems, like mangroves and seagrasses. These habitats sequester large amounts of carbon, helping mitigate climate change by reducing atmospheric CO2 levels.
Thermokarst lakes form from melting permafrost. As they release trapped greenhouse gases like methane, they accelerate climate change.
Fisheries and aquaculture involve the breeding, raising, and harvesting of fish and other aquatic life. Climate change impacts these sectors by altering water temperatures, ocean acidity, and ecosystem balance, threatening food security and livelihoods.
Plant phenology refers to the timing of seasonal biological events in plants, such as flowering, leafing, and fruiting. Climate change alters these timings, disrupting ecosystems and affecting species interactions.
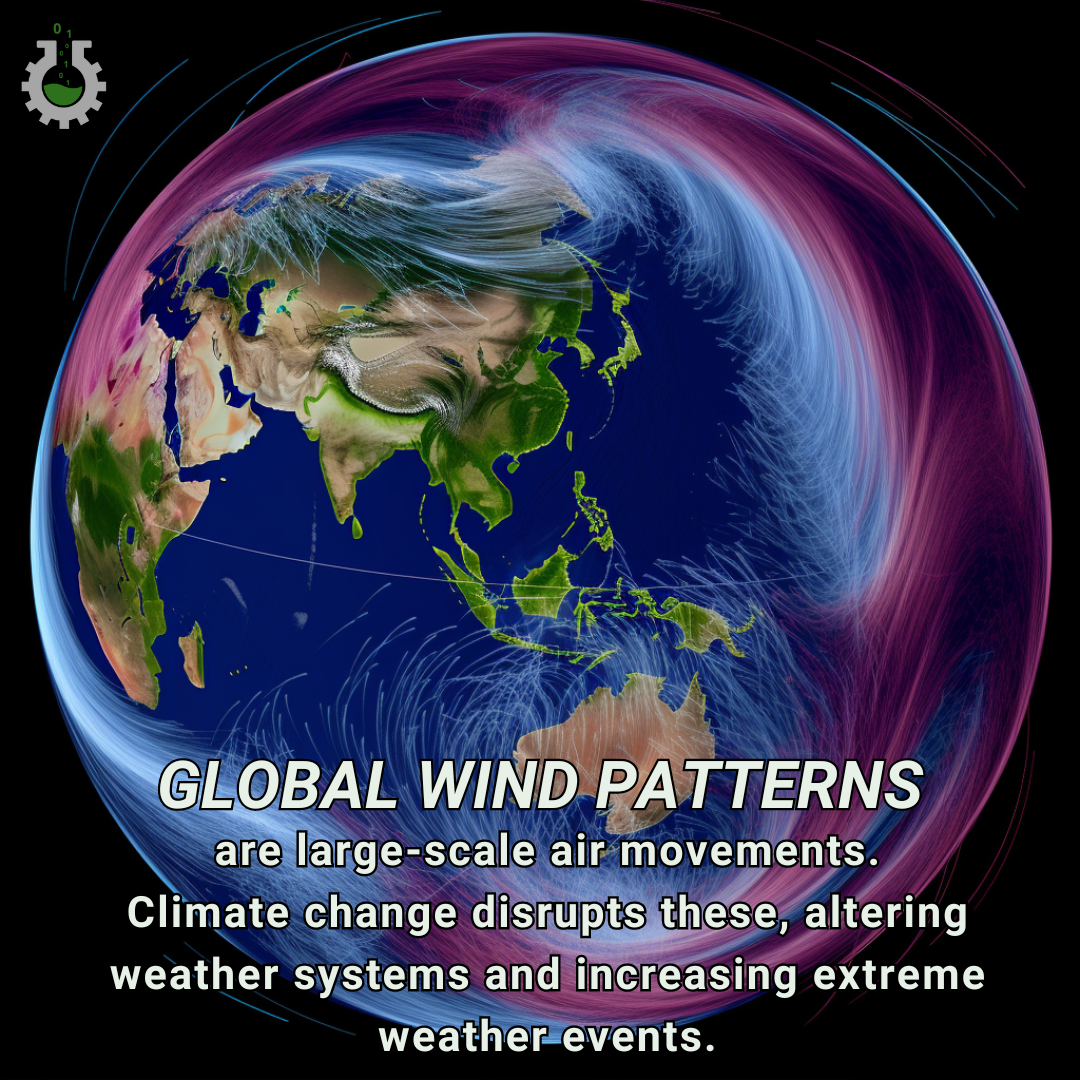
Global wind patterns are large-scale air movements caused by the Earth’s rotation and differential heating. Climate change can alter these patterns, leading to shifts in weather systems, affecting agriculture, water supply, and increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events.
Riverine ecosystems are communities of organisms and their habitats along rivers. Climate change affects these ecosystems by altering water temperatures, flow patterns, and precipitation, leading to habitat loss, reduced biodiversity, and changes in species distribution.
Bioengineering: The application of biological principles to develop solutions. In climate change, it focuses on creating technologies like carbon capture and renewable energy to mitigate environmental impact.
Forest Pathogens are diseases and pests that affect trees. Climate change can exacerbate these threats by creating favorable conditions for their spread, weakening forests and disrupting ecosystems.
Cloud Formation is the process by which water vapor condenses into water droplets or ice crystals, creating clouds. Changes in cloud formation can influence climate change by altering the Earth’s radiation balance, either cooling or warming the planet.