Start thinking more like an analyst.
Learn data science, natural language processing, and big data analysis essentials at your own pace.
Climate Change – An Economic Threat with Trillion-Dollar Consequences
The impact of human-driven climate change on the economy is undeniable, with a report predicting a colossal $1.47 trillion in net property value losses. This shocking figure is primarily due to insurance cost increases and changing consumer demand triggered by the threat of climate change.
Major cities like Miami, Jacksonville, Tampa, New Orleans, and Sacramento are forecasted to bear the brunt of this economic blow. They are on track to witness the largest surges in insurance premiums. Across the U.S., the report anticipates that average insurance premiums will rise by 29.4% by 2055. This includes an 18.4% correction for current underpricing and an additional 11% increase directly linked to climate risk.
The impending crisis is forcing American citizens to reconsider their living choices, with over 55 million expected to move to less climate-vulnerable areas by 2055. This demographic shift will begin sooner than later, with approximately 5.2 million internal climate migrants anticipated by 2025. These numbers underscore the scale of the crisis and the urgency of the response needed.
The report further identifies that fast-growing cities in the South, Southeast, and West are at a higher risk. Here, home values are rising more slowly due to the looming threat of climate change. The impact of climate-related events such as extreme heat, wildfires, and flooding is projected to cause significant relocations within the U.S. over the next few decades.
The Sun Belt states, including California, Florida, and Texas, have already witnessed more than their fair share of climate change consequences. These states have borne over 40% of the U.S.’s $2.8 billion in natural disaster costs since 1980. The future seems equally bleak, with insurance premium increases projected over the next 30 years.
The report paints a grim picture of the future for some counties in California, Florida, and Texas. It projects net declines in property values ranging from 10% to 40% by 2055 due to the impacts of climate change.
The evidence is clear – climate change is not just an environmental issue; it’s a significant economic threat. As the world grapples with this reality, it’s crucial to implement proactive measures to mitigate these impacts and safeguard our future.
Science4Data is committed to cut through greenwashing and measure real impact. Join the journey to a sustainable future. Your actions matter.
Rapid Ocean Warming – A Fourfold Spike and the Climate Crisis
Our Earth’s oceans are experiencing an alarming acceleration in warming, with the increase in temperature seeing a fourfold spike in the last four decades. This unsettling trend is primarily due to climate change and a growing energy imbalance.
The rate of sea surface temperature warming has seen a dramatic escalation. In the 1980s, it was a modest 0.1 degrees Fahrenheit per decade. Today, it has risen to a concerning 0.5F, underlining the urgent imperative to address climate change and significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
The oceans are the unsung heroes in our battle against global warming, absorbing approximately 90% of the heat trapped in the Earth’s atmosphere due to greenhouse gases. In fact, around 90% of global warming occurs in the oceans. However, this role is taking a toll on their health and stability.
Evidence of this can be seen in the global ocean temperatures, which hit record highs for 450 consecutive days in 2023 and 2024. A staggering 44% of this record warmth can be attributed to the oceans absorbing heat at an accelerating rate.
This rise in ocean temperatures poses a menacing threat to marine life, and it also causes sea levels to rise due to thermal expansion. This latter phenomenon endangers coastal areas and underscores the urgency to reduce fossil-fuel burning.
Data reveals that the rate of ocean warming has risen to 0.27 degrees Celsius per decade between 2019 and 2023. This is a rate that is four times faster than that of the 1980s.
One of the major drivers of this accelerated ocean warming is the Earth’s growing energy imbalance. This imbalance is due to increased greenhouse gas concentrations and reduced reflection of sunlight back to space.
A recent study suggests an even more unsettling possibility: the rate of ocean warming over the next 20 years could exceed that observed over the past 40 years. This potential scenario stresses the need for an urgent reduction in fossil fuel burning. If we want to prevent further rapid temperature increases and stabilize the climate, we must act now to curb our fossil fuel consumption and invest in renewable energy sources.
Science4Data is committed to cut through greenwashing and measure real impact. Join the journey to a sustainable future. Your actions matter.
The Power of Multi-Agent AI: Boosting Efficiency and Innovation
In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence, businesses are on the lookout for smarter, more efficient solutions that not only solve complex problems but also scale with their growing needs. Enter Multi-Agent AI Systems—a revolutionary approach to AI where a network of autonomous or semi-autonomous agents work together to achieve specific goals. These intelligent systems are transforming industries by tackling challenges that require coordination, adaptability, and scalability—traits that are crucial for businesses looking to stay ahead in today’s dynamic landscape.
What Are Multi-Agent AI Systems?
At its core, Multi-Agent AI Systems consist of intelligent software agents that can act autonomously or in collaboration to solve complex tasks. These agents operate independently but can also communicate and cooperate when necessary, working towards shared goals. The magic of multi-agent systems lies in their ability to decentralize decision-making, which leads to greater flexibility and scalability in solving real-world problems.
Imagine a team of experts—each with their own area of expertise—working together to tackle a larger problem. This is how multi-agent systems operate. They can be used to handle everything from managing a supply chain to personalizing content and even making real-time predictions based on massive datasets.
Key Features and Benefits of Multi-Agent AI Systems
1. Autonomy: Empowering Independent Decision-Making
One of the standout features of Multi-Agent AI Systems is autonomy. Each agent in the system can operate independently, making decisions based on its local environment or state. This decentralized approach means that agents do not rely on a central controller to function, enabling distributed decision-making that’s more efficient and scalable. This autonomy ensures that agents can handle tasks simultaneously, speeding up processes and reducing bottlenecks.
2. Collaboration: Harnessing the Power of Teamwork
While each agent operates autonomously, collaboration is a key component when tasks require more than one agent. For example, in customer service, different agents may handle various aspects of a conversation—one may provide technical assistance, while another handles billing inquiries. Together, they work to deliver a seamless, personalized experience for the customer. Collaboration among agents also enables them to combine their strengths and tackle larger, more complex problems effectively.
3. Decentralization: Enhancing Efficiency and Resilience
Traditional systems often rely on a centralized control structure, which can become a bottleneck. Multi-agent AI systems, on the other hand, use decentralized decision-making, meaning each agent makes decisions based on its knowledge and local environment. This leads to quicker, real-time responses, particularly in dynamic situations. Decentralization also increases the resilience of the system, as there’s no single point of failure.
4. Adaptability: Evolving in Real-Time
The adaptability of multi-agent systems is one of their most significant advantages. These systems are designed to learn and adjust based on new data and experiences. Agents can evolve their behavior and strategies, making them perfect for fast-paced or unpredictable environments. Whether it’s adjusting to market fluctuations or learning from past customer interactions, adaptability ensures that multi-agent systems stay relevant and effective.
5. Scalability: Growing with Your Business
Scalability is another crucial benefit of multi-agent AI systems. As your business grows, so too can your multi-agent system. Adding new agents to the system is seamless, requiring minimal changes to the underlying structure. This makes multi-agent systems ideal for large-scale applications, such as managing vast amounts of data, optimizing supply chains, or personalizing content for millions of users.
Real-World Applications of Multi-Agent AI Systems
1. Customer Service: Revolutionizing User Interactions
In customer service, multi-agent systems are changing the game. Think about intelligent chatbots that not only handle routine queries but also work with other agents to solve complex problems. Some agents might focus on billing, others on technical support, and still others on order processing. When a customer reaches out, these agents collaborate seamlessly to provide the most accurate and helpful response in the shortest time.
For businesses, this means offering personalized support at scale, with agents that can work 24/7 and continuously learn from each interaction to improve their responses.
2. Content Creation: Enhancing Creativity and Consistency
The content creation industry is another area where multi-agent systems excel. Imagine a system that can autonomously generate, edit, and distribute articles, videos, or social media posts. Different agents can handle different aspects of the content creation process, from brainstorming ideas to proofreading and even personalizing content for different audience segments.
By working together, these agents ensure that the final content is consistent, creative, and high-quality—all while saving time and resources for content teams.
3. Predictive Analytics: Making Data Work for You
In fields like predictive analytics, multi-agent systems can analyze vast datasets to identify trends, detect anomalies, and make forecasts in real time. Different agents specialize in specific types of analysis, such as sentiment analysis, trend forecasting, or anomaly detection, and collaborate to provide the most accurate predictions. This is invaluable for businesses looking to optimize their strategies based on real-time insights.
Overcoming Challenges in Multi-Agent AI Systems
While the benefits of multi-agent AI systems are clear, there are some challenges to consider:
- Coordination: Ensuring that agents work harmoniously without conflicts is crucial. In dynamic environments, managing the interactions between agents can be complex.
- Complexity: Designing and maintaining multi-agent systems is more intricate than traditional centralized systems due to the need to manage multiple agents and their interactions.
- Security: With decentralized decision-making, security is a top priority. Ensuring that agents do not act maliciously or unintentionally introduce vulnerabilities is essential to maintaining system integrity.
As businesses face increasingly complex challenges, Multi-Agent AI Systems are proving to be a game-changer. Their ability to operate autonomously, collaborate seamlessly, and adapt to dynamic environments makes them an invaluable tool across various industries. Whether in customer service, content creation, or predictive analytics, these systems provide businesses with scalable, flexible, and efficient solutions that can tackle even the most complex tasks.
By leveraging the power of multi-agent systems, businesses can stay ahead of the competition, making smarter, faster decisions that drive growth and innovation. While challenges like coordination, complexity, and security remain, the potential for multi-agent AI systems to revolutionize industries is undeniable. Want to harness the power of multi-agent AI? Contact us to learn how!
Climate Change Fuels Global Surge in Urban Rat Infestations
Climate change, a colossal environmental issue of our era, is not only resulting in escalating temperatures, rising sea levels, and worsening floods but also in an unexpected surge of urban rat infestations globally. Increased average temperatures provide an amiable environment for rats to thrive, thereby accelerating the rat population in cities worldwide.
This is not a minor concern as rats pose a significant health risk. They are known to transmit over 50 zoonotic pathogens, which are diseases transmitted from animals to humans. These include serious illnesses such as leptospirosis, hantavirus, and plague. In addition to the physical health risks, rat infestations also contribute to mental health issues, including a heightened risk of depression. Thus, the increasing rat infestations are a clear public health threat that demands immediate attention.
Scientific studies have projected that urban temperatures may rise between 1.9 and 4.4 degrees by 2100 due to greenhouse gas emissions. Such a rise in temperatures can potentially boost rat survival and reproduction rates. A study that observed rat populations in 16 cities globally found increased rat growth trends in most of these cities. The growth was faster in some cities compared to others due to differing rodent control measures.
Cities like Washington, D.C., San Francisco, Toronto, and New York are witnessing a pronounced proliferate in their urban rat populations. The rat infestations are not just a result of climate change, but also due to anthropogenic activities. The responsibility of controlling these burgeoning rat populations falls on both the city and its residents.
There are several strategies that can be implemented to control rat populations. These include securing food waste, which is a primary food source for rats. Ensuring that food waste is properly disposed of or stored can significantly reduce rat populations. Residents are also encouraged to report rat sightings promptly to the city. This allows the city to quickly respond and take appropriate measures to control the rat population.
Another effective strategy is the implementation of integrated pest management. This approach combines various methods to control pests, including the use of pesticides, traps, and preventive measures like sealing off entry points for rats in buildings.
The burgeoning rat population in cities due to climate change is a significant issue that poses serious health risks. It is a responsibility shared by the city and its residents to implement strategies to control this population. As we continue to fight against climate change, we must also be prepared to handle its unexpected consequences, such as the surge in rat populations.
Science4Data is committed to cut through greenwashing and measure real impact. Join the journey to a sustainable future. Your actions matter.
Adapting Apple Production to Climate Change
As the effects of climate change continue to challenge the agriculture sector, researchers are looking for innovative ways to adapt and mitigate potential impacts. In Michigan, a group of researchers have turned their focus to the Malus coronaria, a native apple tree, in their quest to develop frost-resistant apple varieties. The Malus coronaria is known for its late-blooming characteristic, which may provide a valuable trait in the face of changing climate conditions.
At the helm of this research is Steve van Nocker, a plant geneticist at Michigan State University. Van Nocker is working tirelessly to identify the genes responsible for the Malus coronaria’s late blooming. His goal is to develop a genetic stock from these late-blooming genes for use in commercial apple breeding.
The need for such innovative solutions is becoming increasingly critical. A study from Washington State University found that top apple-producing states are experiencing fewer cold days and more warm fall nights. This shift in weather patterns is affecting apple quality and bloom timing, posing potential threats to apple production, quality, and marketability.
In addition to developing frost-resistant varieties, various techniques are being explored to increase apple resilience against climate change. These include utilizing solar panels in vineyards, developing heat-tolerant apple varieties, and constructing unmanned vehicles equipped with heaters.
Climate change is not just about warmer temperatures; it’s also about shifts in weather patterns. Changes in climate conditions such as cold hours and heat accumulation can lead to uneven blooming, crop damage, and increased pest activity in apple production.
To combat these challenges, comprehensive strategies are required. These may include the development of heat-resistant apple varieties and improvements to irrigation systems. Such initiatives are necessary to mitigate climate risks and ensure the sustainability of apple production.
The work of researchers like van Nocker is vital in the face of a changing climate. By harnessing the natural traits of trees like the Malus coronaria, they are paving the way for a more resilient and sustainable future for apple production in the U.S. and potentially, around the world.
Science4Data is committed to cut through greenwashing and measure real impact. Join the journey to a sustainable future. Your actions matter.
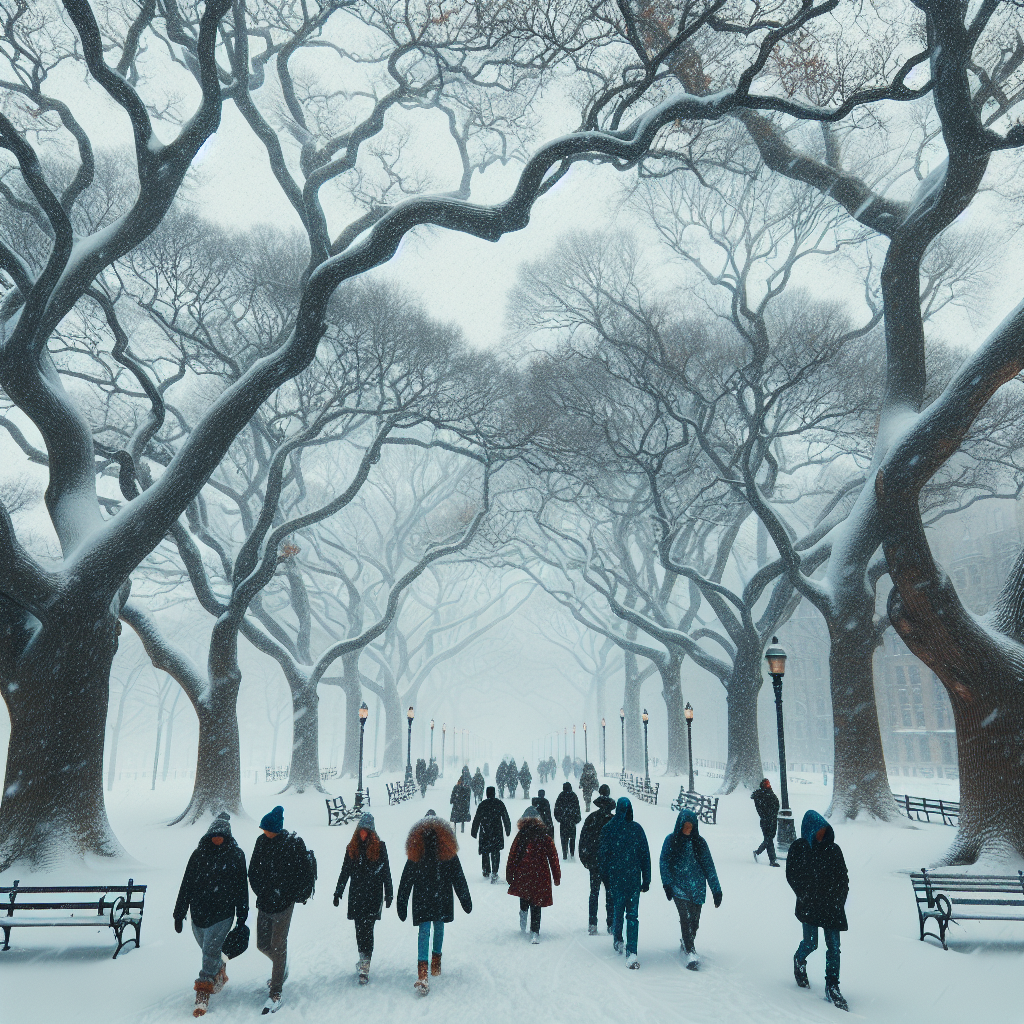
New Orleans’ Record-Breaking Snowstorm and the Impact of Climate Change
New Orleans, a city known for its vibrant culture and hot weather, was recently shaken by an extreme shift in weather conditions. Within just four days, the temperature swung from a comfortable 70 degrees to a record-breaking snowstorm. This unusual weather event was a result of a polar vortex-related Arctic blast, a rare occurrence for the region, which led to the first-ever blizzard warning in Louisiana’s history.
The severe weather blanketed the New Orleans metro area with an unprecedented 10 inches of snow, shattering previous records and leaving residents in awe. But as they grapple with the extreme cold, the city’s inhabitants are also bracing for the upcoming hurricane season, a challenging time that poses its own set of hazards.
Scientists warn that such drastic shifts in the polar vortex, which led to the record snowfall, may become more frequent due to human-induced climate change. This could paradoxically lead to less severe cold over time, making weather patterns increasingly unpredictable.
Interestingly, the Gulf of Mexico, a body of water known for its warm temperatures, may have played a role in the unusual snowstorm. The Gulf has been experiencing unusually high temperatures, and these warmer conditions may have contributed to the record-breaking weather in Louisiana.
The main factors driving the storm were a unique combination of cold air from the Arctic and a rainmaking storm system in the Gulf. The unusually warm waters of the Gulf may have intensified the storm by increasing the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere, a key factor for snow creation.
These recent events serve as a stark reminder of the unpredictable and often extreme shifts in weather that we are experiencing on a global scale. As we continue to navigate these changes, it is more important than ever to prioritize climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies, to safeguard our cities and communities from the impacts of our rapidly changing climate.
Science4Data is committed to cut through greenwashing and measure real impact. Join the journey to a sustainable future. Your actions matter.








